Category:Electoral System Reform: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electoral_reform | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electoral_reform | ||
'''More election systems info at [http://www.fairvote.org/ FairVote]''' | |||
Electoral reform in electoral systems is intended to improve how public desires are expressed in election results. | |||
Popular reforms can include: | |||
Voting systems, such as '''proportional representation''', a '''two-round system (runoff voting)''', '''instant-runoff voting'''... '''citizen initiatives and referendums''' and '''recall elections'''... | |||
Improved voting can include: | |||
*Ballot Access (see [http://ballot-access.org/ Ballot Access News] for more info re: US fed/state election law news) | |||
*Vote-counting procedures | |||
*Rules about political parties, typically changes to election laws | |||
*Eligibility to vote / Factors which affect the rate of voter participation (and counter to improved electoral reforms, often eligibility rules are employed that reduce participation and voter turnout. | |||
*How candidates and political parties are able to stand (nomination rules) and how they are able to get their names onto ballots (ballot access) | |||
*Electoral constituencies and election district borders ('gerrymandering', i.e. skewing the drawing of district boundaries to fit partisan goals, is often utilized and runs counter to full and fair voter participation and representation) | |||
*Ballot design and voting equipment | |||
*Scrutineering (election monitoring by candidates, political parties, etc.) | |||
*Safety of voters and election workers | |||
*Measures against bribery, coercion, and conflicts of interest | |||
*Financing of candidates' and referendum campaigns | |||
Revision as of 20:11, 26 April 2016
- Election Reform
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electoral_reform
More election systems info at FairVote
Electoral reform in electoral systems is intended to improve how public desires are expressed in election results.
Popular reforms can include:
Voting systems, such as proportional representation, a two-round system (runoff voting), instant-runoff voting... citizen initiatives and referendums and recall elections...
Improved voting can include:
- Ballot Access (see Ballot Access News for more info re: US fed/state election law news)
- Vote-counting procedures
- Rules about political parties, typically changes to election laws
- Eligibility to vote / Factors which affect the rate of voter participation (and counter to improved electoral reforms, often eligibility rules are employed that reduce participation and voter turnout.
- How candidates and political parties are able to stand (nomination rules) and how they are able to get their names onto ballots (ballot access)
- Electoral constituencies and election district borders ('gerrymandering', i.e. skewing the drawing of district boundaries to fit partisan goals, is often utilized and runs counter to full and fair voter participation and representation)
- Ballot design and voting equipment
- Scrutineering (election monitoring by candidates, political parties, etc.)
- Safety of voters and election workers
- Measures against bribery, coercion, and conflicts of interest
- Financing of candidates' and referendum campaigns
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-
Electoral System / Representation Issues
http://represent.us/TheProblem
http://represent.us/TheSolution
-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) / ‘ranking the candidates’ systems are used in California and Minnesota, among many other locations.
Cities that use RCV in California include Oakland (http://www.acgov.org/rov/rcv/), Berkeley, San Leandro and San Francisco (http://www.sfelections.org/demo/). Cities in Minnesota that use RCV include St. Paul (http://votestpaul.org) and Minneapolis (http://vote.minneapolismn.gov/rcv/index.htm0)
A proportional representation form of RCV for multi-candidate elections is used in Cambridge, Massachusetts (https://www.cambridgema.gov/election2015/ccouncil/15CouncFinal%20Round15.htm).
Countries that use the system include Australia (http://www.eca.gov.au/systems/proportional/), Ireland (http://www.environ.ie/sites/default/files/publications/files/guide_to_ireland_pr-stv_system_0.pdf), and Scotland (http://www.gov.scot/Topics/Government/Elections/guidance/VotingSystems2).
Subcategories
This category has the following 17 subcategories, out of 17 total.
B
C
D
E
G
I
M
R
V
Pages in category "Electoral System Reform"
The following 16 pages are in this category, out of 16 total.
Media in category "Electoral System Reform"
The following 70 files are in this category, out of 70 total.
- 800000 signatures.png 627 × 114; 24 KB
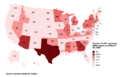
- Access to Voting US-2015.png 560 × 700; 316 KB
- American Legislative Exchange Council.jpg 646 × 143; 41 KB
- At Poynter, St Petersburg, Florida.png 640 × 345; 555 KB
- Biden - will we choose democracy.png 448 × 168; 30 KB
- Biden delivers voting rights speech in Atlanta.png 600 × 679; 387 KB
- Biden voting rights speech attacked by McConnell.png 600 × 321; 142 KB
- Biden voting rights support fading.png 600 × 682; 386 KB
- Billy Tauzin via Moyers-Potter-Penniman Nation on the Take.jpg 800 × 450; 82 KB
- Cassidy Hutchinson testifies at Congressional committee hearing.png 640 × 447; 200 KB
- Dark Money Book FOC.jpg 408 × 630; 73 KB
- David Bossie Money in Politics-CSpan.jpg 640 × 336; 24 KB
- Dollar-Sign m.png 235 × 235; 10 KB
- EleanorRooseveltHumanRights.png 535 × 423; 60 KB
- ElectionResources.png 607 × 243; 141 KB
- Electoral Count Reform Act - US, Brennan Center 2023.png 749 × 1,611; 339 KB
- Electoral Reform US FairVote.jpg 662 × 270; 36 KB
- European Greens - Baerbock - Candidate for German Chancellorship.jpg 513 × 185; 37 KB
- European Greens EGPCongress Dec 2022.png 800 × 745; 640 KB
- FairVote.jpg 535 × 122; 14 KB
- German foreign minister travels to India.png 640 × 178; 115 KB
- Gov and money.jpg 240 × 210; 7 KB
- Greeneuropeanjournal.eu.jpg 485 × 237; 30 KB
- How Gerrymandering Works via Wonkblog.png 640 × 473; 226 KB
- January 6 committee - on December 19 2022.png 640 × 468; 591 KB
- January 6 committee final hearing - news.png 600 × 661; 343 KB
- January 6 committee votes to issue criminal referrals against Trump.png 800 × 204; 458 KB
- June 28 2022.png 800 × 565; 300 KB
- Manual Audits needed.png 557 × 480; 148 KB
- Methods of Nonviolent Action.pdf ; 49 KB
- Monarch Bay Hotel 1.jpg 700 × 495; 115 KB
- Money in Politics - PoliticoPay.png 491 × 226; 31 KB
- Money in Politics-System Failure-JLawrence Vid 2019.jpg 496 × 501; 44 KB
- Money-in-Politics Books 2012-16.png 479 × 756; 566 KB
- Moneyovercongress.jpg 175 × 80; 4 KB
- OhClarence - Google News - Aug 10, 2023.png 800 × 856; 391 KB
- OhClarence 2 - Google News - Aug 10, 2023.png 800 × 819; 461 KB
- OhClarence 3 - Google News - Aug 10, 2023.png 800 × 842; 473 KB
- OhClarence 4- Google News - Aug 10, 2023.png 800 × 853; 491 KB
- One year later...I will defend this nation Jan-6-2022.png 513 × 364; 238 KB
- Plutocrats United Hasen.jpg 206 × 293; 15 KB
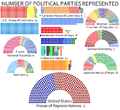
- Political parties represented 2015.png 720 × 658; 441 KB
- President Biden - January 5, 2024.png 600 × 470; 236 KB
- President Biden speaks of protecting democracy - Jan 5 2024.png 600 × 686; 214 KB
- President Biden speaks of protecting democracy - News on Jan 5 2024.png 600 × 664; 351 KB
- Presidential Ballot Access US 2016 cycle.png 800 × 692; 131 KB
- Protect Democracy.png 775 × 600; 727 KB
- Richard Jacobs and The Man in the Arena - on July 4 2022.png 800 × 380; 192 KB
- Rise of Partisanship in US Congress.png 800 × 437; 178 KB
- Roosevelt and Muir at Yosemite.png 503 × 694; 686 KB
- SCOTUS-and the curtain re ABA.jpg 800 × 401; 152 KB
- SunlightFoundation-logo.png 198 × 70; 10 KB
- The Great Hack.jpg 640 × 395; 73 KB
- The Oath and the Office.png 572 × 480; 151 KB
- Trump on Termination of US Constitution - 1.jpg 600 × 607; 166 KB
- Trump on Termination of US Constitution - 2.jpg 600 × 600; 181 KB
- Trump on Termination of US Constitution - 3.PNG 600 × 600; 227 KB
- US Party Identification 88 to 14.jpg 494 × 314; 27 KB
- US Senate debates voting rights bill.jpg 640 × 461; 107 KB
- VOTE.jpg 369 × 311; 40 KB
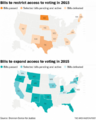
- Voting restriction bills 3-24-2021.png 640 × 409; 78 KB
- Voting Wars.jpg 220 × 347; 80 KB
- When-money-talks cressman-book-jacket.png 184 × 293; 97 KB
- Your vote.png 318 × 133; 11 KB
- Youth vote estimates 2016 primary.png 800 × 490; 257 KB