TinyBlueGreen: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
○ | ○ | ||
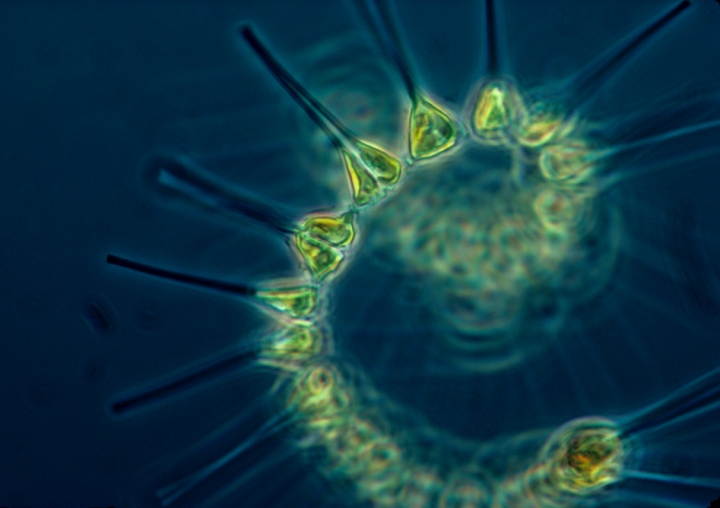
<big><big>'''Phytoplankton/Diatoms/Algae -- Microorganisms of the Oceans'''</big></big> | <big><big>'''''Phytoplankton/Diatoms/Algae -- Microorganisms of the Oceans'''''</big></big> | ||
[http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/File:Phytoplankton.jpg Phytoplankton] | [http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/File:Phytoplankton.jpg ''Phytoplankton: "Climate Dance"''] | ||
Revision as of 02:14, 13 February 2016
Blue-Green & Life
- "A single kind of blue-green algae in the ocean produces the oxygen in one of every five breaths we take"
- ~ from "The World Is Blue: How Our Fate and the Ocean’s Are One" by Sylvia Earle
"The Tiny Little Ones"
- "The grasslands of the sea"
It is estimated that marine plants produce between 70 and 80 percent of the oxygen in the atmosphere. Nearly all marine plants are single celled, photosynthetic algae... plankton
Marine Algae: The Most Important Organism?
○
Ocean Grasslands and Forests"
Planet Citizens, Planet Scientists Study Ocean Forests
○
2016
Big Trouble Ahead for Ocean Plankton
○
References
Wikipedia -- Phytoplankton obtain energy through the process of photosynthesis and must therefore live in the well-lit surface layer (termed the euphotic zone) of an ocean, sea, lake, or other body of water. Phytoplankton account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth.
Phytoplankton are responsible for much of the oxygen present in the Earth’s atmosphere – half of the total amount produced by all plant life.
See Prochlorococcus
Cyanobacteria /saɪˌænoʊbækˈtɪəriə/, also known as Cyanophyta, is a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis.[4] The name "cyanobacteria" comes from the color of the bacteria (Greek: κυανός (kyanós) = blue). They are often called blue-green algae...
- Cyanobacteria are arguably the most successful group of microorganisms on earth. They are the most genetically diverse; they occupy a broad range of habitats across all latitudes, widespread in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems, and they are found in the most extreme niches such as hot springs, salt works, and hypersaline bays. Photoautotrophic, oxygen-producing cyanobacteria created the conditions in the planet's early atmosphere that directed the evolution of aerobic metabolism and eukaryotic photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria fulfill vital ecological functions in the world's oceans, being important contributors to global carbon and nitrogen budgets.
Aquatic cyanobacteria are known for their extensive and highly visible blooms that can form in both freshwater and marine environments. The blooms can have the appearance of blue-green paint...
Cyanobacteria use the energy of sunlight to drive photosynthesis, a process where the energy of light is used to split water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons. Because they are aquatic organisms, they typically employ several strategies which are collectively known as a "carbon concentrating mechanism" to aid in the acquisition of inorganic carbon (CO2 or bicarbonate)...
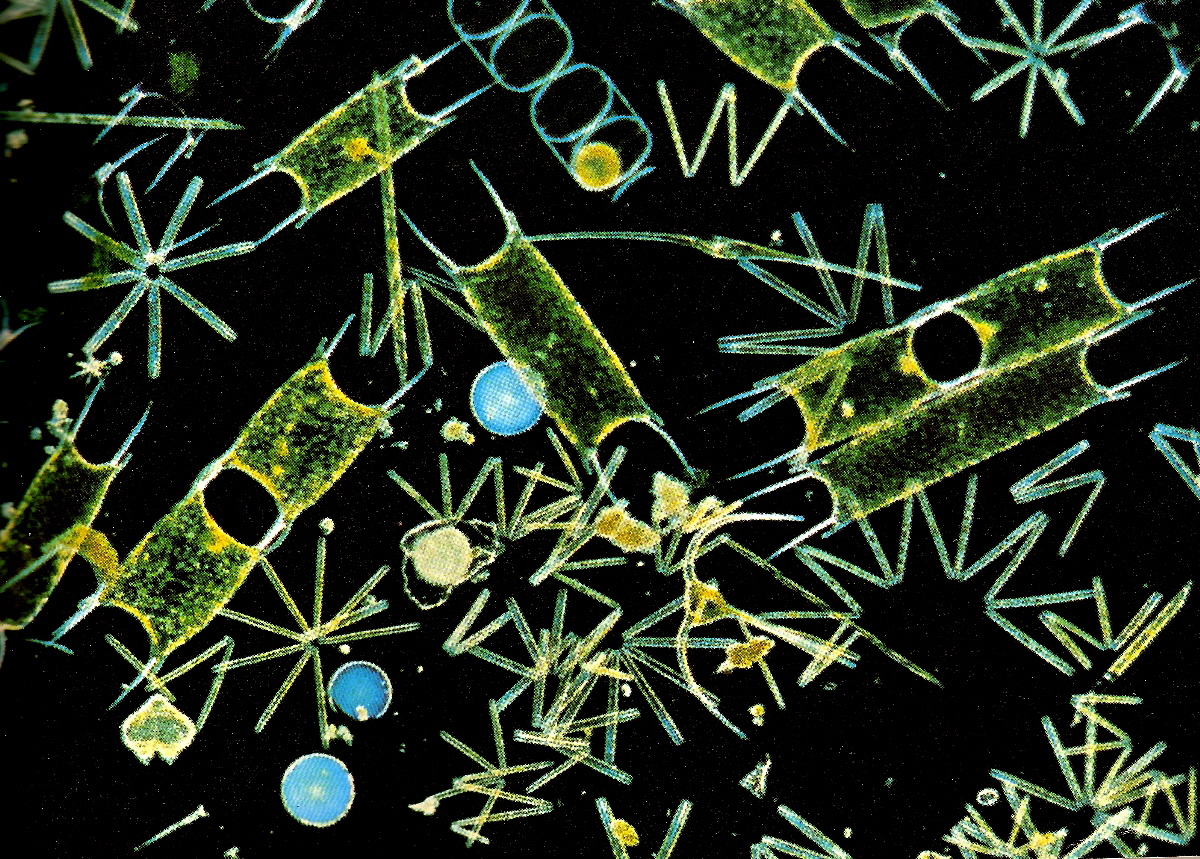
See Diatoms
[Diatoms are] among the most common types of phytoplankton. Diatoms play an important role in biogeochemical earth because they contribute an estimated 75% of primary production in coastal waters... There are more than 200 genera of living diatoms, and it is estimated that there are approximately 100,000 extant species.
○
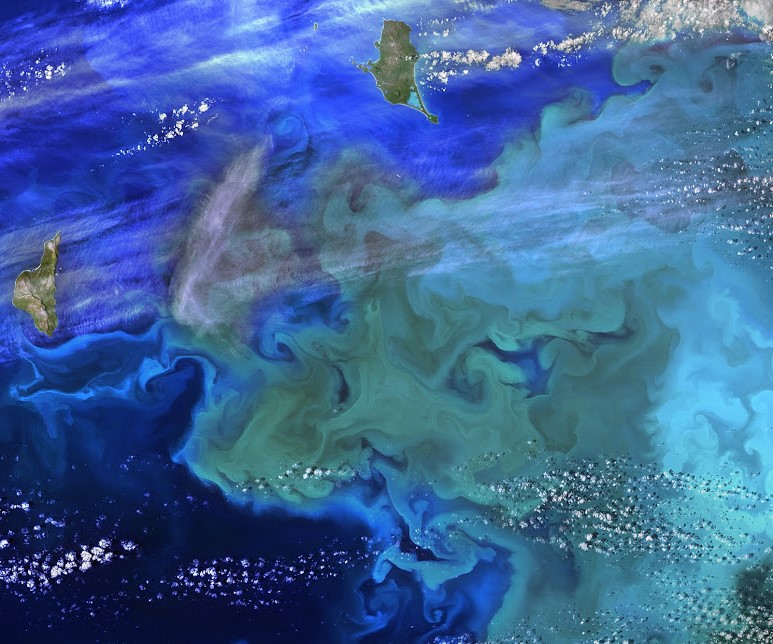
Phytoplankton/Diatoms/Algae -- Microorganisms of the Oceans
Phytoplankton: "Climate Dance"
~ Phytoplankton account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth
○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○
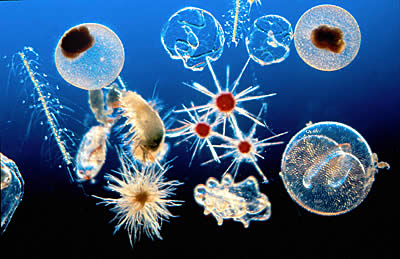
Endangered Tiny-Miniscule Species
GP360: The standard approach, when looking at threatened species, is to focus on well-known larger species. The Red List is widely known for its work to identify species at risk of extinction. Its work forms the basis for many biodiversity preservation efforts. The focus on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_world's_100_most_threatened_species larger, readily identified animals is the norm and these species, often mammals, provides just a part of the larger picture of our threatened environment.
Large 'charismatic', or 'iconic' species, most often eclipse recognition of rarely considered species that are not even 'known' or known to be in danger...
The reality is that much of the extinction in our era is of the small species, the lesser known, unknown and unconsidered species, whether in the rich biospheres of the rainforest or the oceans, the micro-organisms are at risk and in peril of collapse.
When we speak of Plankton, as a profoundly critical keystone species, the food chain of the oceans begins with plankton, yet the disruption of the atmosphere and the heating of the ocean, or acidification, will have great consequences to the Phytoplankon, flagellates who cannot move with their limited locomotion system... Acidification of the oceans and the increases of heat or strengthened suns rays due to changes in atmospheric conditions and UV radiation can have deadly consequences to the 'least of and smallest of' the species -- and as a result effect the larger systems in ways that science is only now beginning to measure and monitor.
We are, our species is, beginning to understand that as the small animals comprising the foundations of the 'food chain' and biosphere systems are disrupted, endangered and/or destroyed, the rest of the food chain and integral ecological connections between species will be disrupted, endangered, and/or destroyed.
This is a great challenge of the era in which we live... loss of biodiversity and a 'ripple effect' over time, a threat environment that demands strategic environmental security as a key goal, as a policy objective beginning with awareness and policies and practices of sustainability.
○
SMALL v LARGE SPECIES
Phytoplankton obtain energy through the process of photosynthesis and must therefore live in the well-lit surface layer (termed the euphotic zone) of an ocean, sea, lake, or other water.
Phytoplankton account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth...
Phytoplankton are responsible for much of the oxygen present in the Earth’s atmosphere – half of the total amount produced by all plant life. - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phytoplankton
○
Marine Biodiversity Strongly Linked to Ocean Temperature
ScienceDaily / 2010 — In an unprecedented effort published online by the international journal Nature, a team of scientists mapped and analyzed global biodiversity patterns for over 11,000 marine species ranging from tiny plankton to sharks and whales.
The researchers found striking similarities among the distribution patterns, with temperature strongly linked to biodiversity for all thirteen groups studied. These results imply that future changes in ocean temperature, such as those due to climate change, may greatly affect the distribution of life in the sea.
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/07/100728131707.htm
○
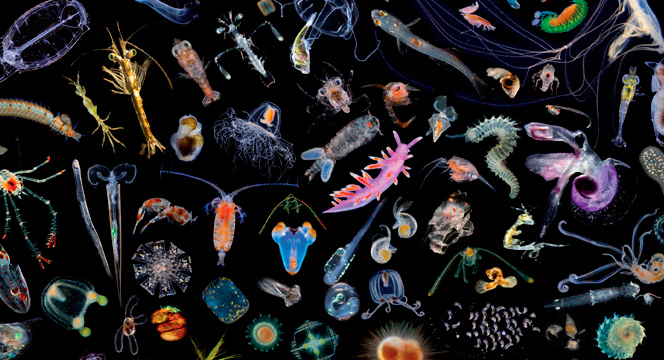
Plankton
2015 - Big Trouble Ahead for Ocean Plankton
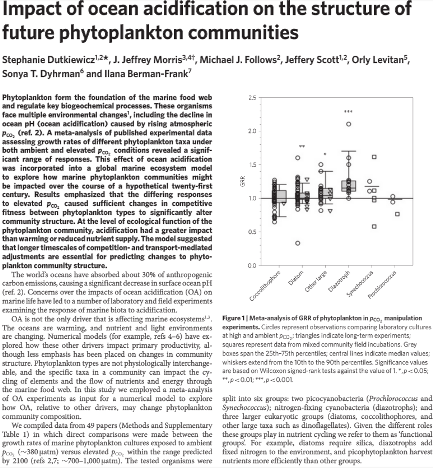
Sobering news: Ocean acidification will likely kill off some phytoplankton species and let others thrive, while warming waters will likely cause mass phytoplankton migrations toward the poles. In short: The base of the marine food web could be in for some serious upheaval in the coming decades. Here’s more from MIT News:
“I’ve always been a total believer in climate change, and I try not to be an alarmist, because it’s not good for anyone,” says (Dr. Stephanie) Dutkiewicz, who is the paper’s lead author. “But I was actually quite shocked by the results. The fact that there are so many different possible changes, that different phytoplankton respond differently, means there might be some quite traumatic changes in the communities over the course of the 21st century. A whole rearrangement of the communities means something to both the food web further up, but also for things like cycling of carbon.”
Dutkiewicz and her colleagues studied 154 published experiments...
GLOBAL PLANKTON WATCH SECCHI DISK
THE GLOBAL SEAFARER STUDY OF THE MARINE PHYTOPLANKTON
ABOUT THE PROJECT
The phytoplankton in the sea account for approximately 50% of all photosynthesis on Earth and, through the food web they support, they underpin the marine food chain.
Living at the surface of the sea the phytoplankton are particularly sensitive to changes in sea surface temperature.
We need to know much more about these changes and you can help by making a simple piece of scientific equipment called a Secchi Disk and using the free Secchi App.
Full instructions for the project are included in the free Secchi App.
Press Release -- Scientists fear the population of the microscopic beings is in decline due to rising sea temperatures and, if true, that could have consequences for every aspect of marine life.
Plankton biologist Dr Richard Kirby, who is leading the study, said: "As the phytoplankton live at the surface of the sea they are being affected by rising sea temperatures due to climate change. A scientific paper published in 2010 suggested the ocean's plankton population had declined by as much as 40 per cent since 1950. Like all marine creatures, phytoplankton have a preferred optimum sea temperature no matter where they are in the world and we need to know more about how they are changing in order to understand the effects on the ocean's biology.” To check the levels of phytoplankton in our oceans, marine experts have developed a free smart phone app for sailors and fishermen to use wherever they are in the world.
Dr Kirby added: "The Secchi Disks are still used by marine scientists to study phytoplankton but there are too few scientists to survey the world's oceans as well as we would wish. This app enables seafarers around the world to take part in a science project and if we can just get a small percentage of the global population of sailors involved, we can generate a database that will help us understand how life in the oceans is changing. It would help us learn much more about these important organisms at a crucial time when their habitat is altering due to climate change."
The Secchi app has been developed by Dr Nicholas Outram and Dr Nigel Barlow, from Plymouth University’s School of Computing and Mathematics, and the database will be maintained by Pixalytics Ltd.
○
Phytoplankton obtain energy through the process of photosynthesis and must therefore live in the well-lit surface layer (termed the euphotic zone) of an ocean, sea, lake, or other body of water. Phytoplankton account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth. Thus phytoplankton are responsible for much of the oxygen present in the Earth’s atmosphere – half of the total amount produced by all plant life. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phytoplankton
○
Marine Biodiversity Strongly Linked to Ocean Temperature
Ocean Temperatures: Are our oceans dying?
"Phytoplankton have declined 40% in 60 years as figures reveal Earth has been getting hotter since the Eighties and much of the heat has been absorbed by oceans...
Microscopic marine algae form the basis of the ocean food chain are dying at a "terrifying rate"...
Phytoplankton, described as the 'fuel' on which marine ecosystems run, are experiencing declines of about 1 per cent of the average total a year...
According to researchers, a 40 per cent drop in phytoplankton since 1950...
Marine diatom cells (Rhizosolenia setigera), an important group of phytoplankton in the oceans are now in massive decline...
The reduction in the amount of algae in the pceams could have an impact on a wide range of species, from tiny zooplankton to marine mammals, seabirds, fish and humans...
The decline of the phytoplankton would be a more dramatic change than the loss of the tropical rainforests, scientist say...
The research, published in the journal Nature, says plankton declines are linked to rising sea-surface temperatures and changes in the conditions of the ocean, particularly close to the equator...
Most of the declines are seen in tropical regions, polar and in the open ocean, where most phytoplankton are produced...
~ ~ ~ ~
Marine food chains at risk of collapse, extensive study of world's oceans finds
Important ecosystems could be massively damaged by 2050 unless greenhouse gas emissions and localised pollution is drastically reduced, researchers say
The food chains of the world’s oceans are at risk of collapse due to the release of greenhouse gases, overfishing and localised pollution, a stark new analysis shows.
A study of 632 published experiments of the world’s oceans, from tropical to arctic waters, spanning coral reefs and the open seas, found that climate change is whittling away the diversity and abundance of marine species.
The paper, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, found there was “limited scope” for animals to deal with warming waters and acidification, with very few species escaping the negative impact of increasing carbon dioxide dissolution in the oceans.
~ ~ ~ ~
Nature Climate Change: Revaluating ocean warming impacts on global phytoplankton
~ ~ ~ ~
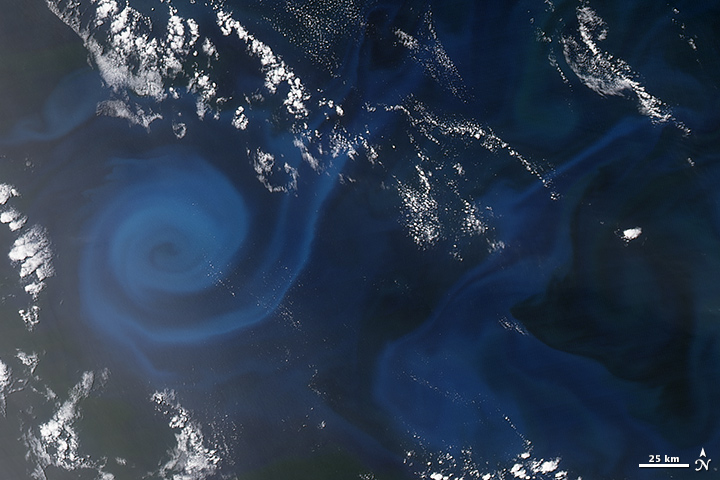
NASA Earth Observatory
Phytoplankton Oxygen Factories
Phytoplankton are the grass of the sea. They are floating, drifting, plant-like organisms that harness the energy of the Sun, mix it with carbon dioxide that they take from the atmosphere, and turn it into carbohydrates and oxygen.
Phytoplankton are critical to the marine food web, being the primary producers of food for the oceanic food web, from zooplankton to fish and shellfish to whales.
Like plants and trees on land, phytoplankton give us a lot more than food. It is estimated that 50 to 80 percent of the oxygen in our atmosphere has been produced by phytoplankton. At the same time, they are responsible for drawing down significant portions of the carbon dioxide from the air. The tiniest of living organisms exert an outsized influence on the planet.
○
Earth Science Research from Space
http://eoimages.gsfc.nasa.gov/images/imagerecords/87000/87465/sepacific_vir_2016013.jpg