File:Hubble-2004-b-full jpg.jpg

Original file (6,672 × 6,340 pixels, file size: 13.86 MB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Click on Original File
1.2-million-galaxies-map-slice.jpg (800 × 600 pixels, file size: 326 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Hubble & Sloan Digital Sky Survey III (SDSS-III)
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/File:1.2-million-galaxies-map-slice.jpg
https://www.sdss3.org/surveys/
https://www.sdss3.org/science/
https://www.sdss3.org/education/
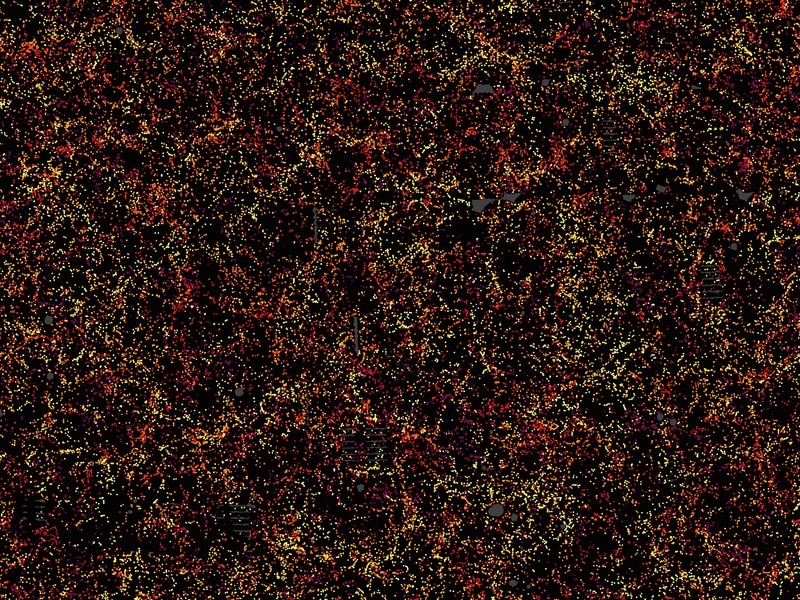
Each dot in the picture at top indicates the position of a galaxy.
The image covers about 1/20th of the sky, a slice of the universe 6 billion light-years wide (thus we see some of these galaxies 6 billion years into the past), 4.5 billion light-years high, and 500 million light-years thick.
http://earthsky.org/space/1-2-million-galaxies-in-3d
July 2016 - The largest three-dimensional map of our universe so far. It’s a map of 1.2 million galaxies over a quarter of the sky and over a volume of space of 650 cubic billion light-years.
Sloan Digital Sky Survey -- https://www.sdss3.org/
______________________________________________
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/mw/images/Hubble-2004-b-full_jpg.jpg
Hubble - http://hubblesite.org/
http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/xdf.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NQhaKVifhjI
http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Hubble
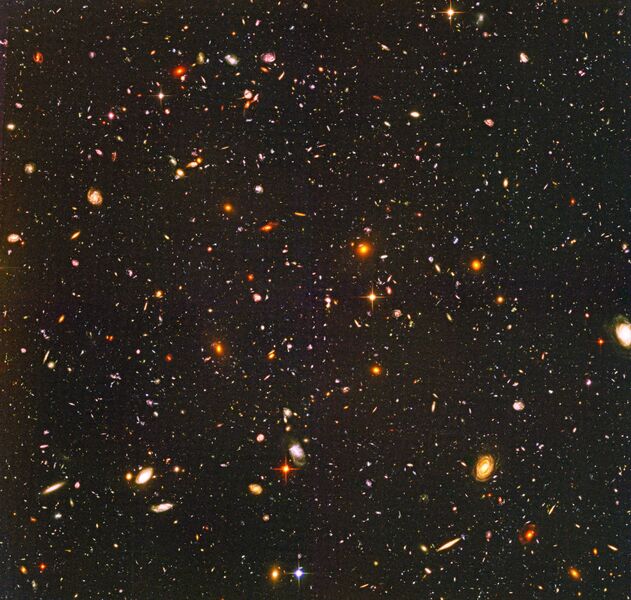
Hubble Goes to the eXtreme to Assemble Farthest-Ever View of the Universe
Sept 2012 -- Like photographers assembling a portfolio of best shots, astronomers have assembled a new, improved portrait of mankind's deepest-ever view of the universe.
http://certificate.ulo.ucl.ac.uk/HUDF.html
http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2004/07
http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2004/07/image/a/
http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/survey/hubble-ultra-deep-field/2014/27/fastfacts/
○
JUNE 2014
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured the most colorful and detailed image of the early universe — officially dubbed the Ultra Deep Field 2014 — with galaxies that date back to just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. While many of the blobs in the photo might look like stars, every single point of light is an entire galaxy — around 10,000 of them, in case you were wondering — each containing millions or billions of stars. The photo is the culmination of over 10 years of observations, totaling around 600 hours of exposure time, made during 841 orbits of the Earth.
If the Ultra Deep Field (UDF) looks familiar, it’s because you’ve seen its predecessor, the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF). Both images are of the exact same (tiny) piece of night sky in the southern hemisphere’s Fornax constellation. The UDF is actually very similar, and uses much of the same imagery that was composited to create the XDF, but with one very interesting addition: Ultraviolet light.
Basically, Hubble has a number of imaging devices (cameras) that are specifically tailored towards a specific task or spectrum of light. The previous image, the XDF, only used visible and infrared imagery captured by Hubble’s ACS Wide Field Channel and newer Wide Field Camera 3’s IR sensor. The new UDF photo, however, also includes imagery from the WFC3’s 16-megapixel ultraviolet CCD. In scientific terms, light spectrum captured by the original XDF ranges from 350nm to 1700nm, while the UDF is from 200nm to 1700nm.
What does that extra 150nm of ultraviolet light get you? Quite a lot, according to Hubble’s crack team of astronomers. Ultraviolet light is primarily produced by the hottest, largest, and youngest stars. Without UV, the astronomers were unable to accurately work out which galaxies were forming the most stars — which, when you’re looking at a photo that chronicles a period just a few million years after the Big Bang, is pretty vital information. “The lack of information from ultraviolet light made studying galaxies [in the XDF] like trying to understand the history of families without knowing about the grade-school children,” says principal investigator Harry Teplitz of Caltech in Pasadena, California. “The addition of the ultraviolet fills in this missing range.”
Hubble’s new-found ability to capture UV light (it was only enabled by the 2009 delivery of the WFC3 by Space Shuttle Atlantis) is unique, as far as space telescopes go. Even when Hubble’s successor, the James Web Space Telescope (JWST) is launched, astronomers will still rely on Hubble’s UV imaging chops (JWST will only capture infrared light, with the hope of capturing a glimmer of light from the universe’s first stars).
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 14:40, 25 April 2015 |  | 6,672 × 6,340 (13.86 MB) | Siterunner (talk | contribs) | Hubble - http://hubblesite.org/ http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/xdf.html https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NQhaKVifhjI http://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/Hubble Hubble Goes to the eXtreme to Assemble Farthest-Ever View of the Universe ... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: