Category:Ecoregions
<addthis />
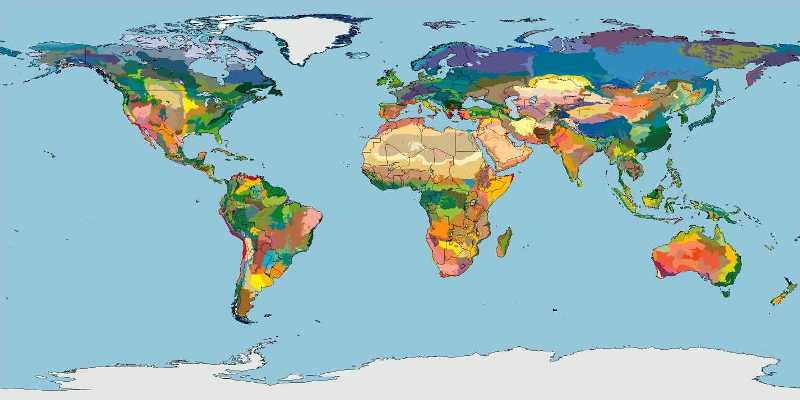
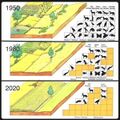
Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth
Via BioScience / The tapestry of life on Earth is unraveling as humans increasingly dominate and transform natural ecosystems. Scarce resources and dwindling time force conservationists to target their actions to stem the loss of biodiversity — a pragmatic approach, given the highly uneven distribution of species and threats (Soulé and Kohm 1989, Olson and Dinerstein 1998, Mace et al. 2000, Myers et al. 2000). Unfortunately, the ability to focus strategically is hindered by the absence of a global biodiversity map with sufficient biogeographic resolution to accurately reflect the complex distribution of the Earth’s natural communities.
GreenPolicy360 recognizes that humankind, in a new Anthropocene era, is exploring in an initial phase of discovery of life systems on Earth, terrestrial and oceans, in forest canopies and microbial soil, and atmospheric currents and conditions that are only now beginning to be studied over time with research from space earth science missions.
Many life enabling systems are only now being seen for what they are:
"A single kind of blue-green algae in the ocean ('Prochlorococcus') produces the oxygen in one of every five breaths we take"
'Tiny little ones' that go unseen and undiscovered, in every ecoregion and biosphere, are coming into view and, given the connectivity of life systems, science is beginning to sense and study how ecoregional life can be essential to global sustainability.
Phytoplankton, the multitude of tiny creatures throughout oceans, the basis of the ocean food chain and in danger of climate change effects, account for half of all photosynthetic activity on Earth... Phytoplankton are responsible for much of the oxygen present in the Earth’s atmosphere, half of the total amount produced by all plant life. Phytoplankton are the foundation of the oceanic food chain and they are the ocean food chain's weak link: "Tiny Ocean Plants Are Dying Off.
Like most all of the microbial life that enriches soil and makes agriculture possible, the life in the sea goes unnoticed and for the greatest part goes unstudied as the impacts from anthropogenic activities escalate.
Humans, homo sapiens on a Tree of Life, are only now beginning to discover and protect the extent of biodiversity in ecoregions.
https://www.greenpolicy360.net/w/File:Tree_of_Life_opensourcetreeoflife.jpg
○
○
Ecoregions via Encyclopedia of Earth
○
Ecoregions & Extinction: Environments & Existence
Subcategories
This category has the following 3 subcategories, out of 3 total.
Pages in category "Ecoregions"
The following 23 pages are in this category, out of 23 total.
S
Media in category "Ecoregions"
The following 126 files are in this category, out of 126 total.
- AB 2480 Meadows and Forest Water Infrastructure.png 481 × 375; 248 KB
- About Baselines and Change.png 592 × 312; 33 KB
- Against the Tide by Cornelia Dean.jpg 600 × 800; 265 KB
- Algae release -nikon-small-world-competition-2017-winners.jpg 640 × 576; 89 KB
- All species day with homo sapien in Santa Fe .jpg 640 × 369; 98 KB
- Bill Mollison 1928-2016.pdf ; 99 KB
- Bill Mollison courtesy of Permaculture magazine.jpg 460 × 300; 0 bytes
- Bill Mollison the day after his passing memories.png 1,381 × 651; 1.65 MB
- Bug eyes in the rainforest canopy Photo by Don Perry-2.jpg 300 × 576; 24 KB
- California's kelp forests and coastal biodiversity diminished.png 532 × 754; 307 KB
- Celebrating 50 Years of Landsat.png 600 × 610; 909 KB
- Celebrating Earth's Beauty 2015.png 1,150 × 716; 1.53 MB
- Chasing Coral.jpg 800 × 437; 65 KB
- Connect with Nature.png 405 × 280; 17 KB
- CopernicusEU - Sentinel5P Atmosphere Monitoring Mission - 2.jpg 795 × 1,477; 654 KB
- CopernicusEU - Sentinel5P Atmosphere Monitoring Mission.png 583 × 465; 222 KB
- Coral bleaching Great Barrier Reef 2016.jpeg 630 × 472; 91 KB
- Coral growing-Mott Lab,Florida.jpg 800 × 382; 114 KB
- Coral reef rejuvenation-montage.png 569 × 236; 318 KB
- Cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus worldmapping MIT.jpg 473 × 321; 60 KB
- Discovery Center, St Pete Pier, Living Shorelines.jpg 800 × 530; 118 KB
- Don Perry SmithsonianCover.jpg 700 × 967; 873 KB
- DSCOVR EPIC - July 20 2022.png 532 × 612; 315 KB
- Earth AI - Feb 2022.png 482 × 480; 192 KB
- Earth Information Center - 2022 Graphic NASA.png 800 × 981; 868 KB
- Earth Information Center from NASA.jpg 800 × 577; 94 KB
- Earth Observing System - fleet of satellites.png 740 × 576; 557 KB
- Earth POV from the ISS Cupola-m.jpg 800 × 480; 71 KB
- Earth System Observatory-1.jpg 580 × 833; 129 KB
- Earth System Observatory-2.jpg 580 × 831; 69 KB
- Earth Viewing from the International Space Station.jpg 496 × 307; 45 KB
- EarthDecadel Priorities-2018.jpg 779 × 529; 85 KB
- Ecoregions of the World terrestrial-wiki.jpg 800 × 400; 33 KB
- Ecostress Mission-Aug 2020.jpg 640 × 311; 85 KB
- ECOTRAM - Don Perry.png 800 × 474; 390 KB
- Elephant herd from the End of the Game-by Peter Beard.jpg 800 × 544; 198 KB
- EO and Fire Ants in the US - on World Wildlife Day.png 768 × 811; 663 KB
- Eukaryotic Cell SCU.jpg 716 × 1,024; 799 KB
- Fire Ants.png 601 × 600; 603 KB
- Floating Forest Project .png 773 × 461; 932 KB
- Global Biodiversity Information-Data.png 501 × 266; 124 KB
- Great Barrier Reef dying.jpg 1,920 × 1,280; 706 KB
- Great Barrier Reef severe bleaching die-off.png 704 × 388; 630 KB
- Great-barrier-reef-2011 image credit, mike mccoy.jpg 2,560 × 1,600; 3.91 MB
- Haiku poems - Owl against a dusk sky - via Haiku Foundation.png 514 × 413; 144 KB
- Haikubox via RM citizen science.png 600 × 640; 466 KB
- How satellites monitor climate change circa 2016.png 599 × 327; 0 bytes
- INaturalist butterfly.jpg 1,024 × 683; 202 KB
- Jane Goodall.png 699 × 642; 443 KB
- July 14, 2018 - hello down there.png 524 × 467; 290 KB
- Kelp NOAA credit Robert Schwemmer.jpg 450 × 299; 193 KB
- Land Remote Sensing Policy Act of 1992.jpg 563 × 480; 144 KB
- LANDSAT - NASA.jpg 622 × 415; 95 KB
- Landsat 9 about to launch.png 420 × 721; 355 KB
- Landsat 9 Launches - 1.jpg 600 × 693; 128 KB
- Landsat 9 Launches - 2.jpg 600 × 737; 250 KB
- Landsat band imagery2.png 800 × 400; 907 KB
- Landsat data site.png 657 × 600; 499 KB
- Landsat launched 50 years ago today.png 528 × 779; 755 KB
- Landsat memories.png 535 × 473; 159 KB
- Landsat NASA - Feb 11 2023.png 763 × 600; 578 KB
- Landsat US collection of maps 1985-2021.png 768 × 775; 1,018 KB
- Landsat, a 50 year legacy.png 528 × 575; 288 KB
- Launch into Space.jpg 800 × 717; 50 KB
- Living Diversity or Not in Your Home Yard.png 436 × 640; 582 KB
- Living-Shoreline.png 800 × 367; 128 KB
- LivingShorelines Graph.png 680 × 375; 73 KB
- Mangroves 'green wall' in China.png 600 × 600; 466 KB
- Mangroves and Coastal Wetlands tracked by Landsat.png 600 × 716; 245 KB
- Mapping the Earth with Google Earth Outreach.jpg 640 × 648; 109 KB
- Mares Kelp 3.png 903 × 476; 869 KB
- Mares Kelp.png 903 × 476; 532 KB
- MLT Geospace - the Edge.jpg 800 × 600; 22 KB
- Mysterious circles around the world.png 733 × 600; 655 KB
- NASA Launch of Landsat 9 - Sept 27, 2021.jpg 675 × 772; 131 KB
- NASA's continuing vision and mission - as of 2005.png 640 × 414; 153 KB
- NASA-Debris-Kessler Syndrome.jpg 750 × 600; 76 KB
- New Species Discovered-2018.png 800 × 212; 508 KB
- Nile River and Mideast.jpg 750 × 929; 87 KB
- Overshoot presentation - Rees 2.png 640 × 246; 81 KB
- Overshoot presentation by Prof William Rees - 2021.jpg 640 × 432; 76 KB
- PACE - NASA Everything on Earth Is Connected.png 600 × 264; 70 KB
- PACE - NASA Jan 17 2024.png 600 × 662; 465 KB
- Permaculture-observation tip.jpg 480 × 540; 86 KB
- Phyto glowing beauty of the oceans.jpg 480 × 265; 20 KB
- Phyto the Green Machine.png 640 × 465; 431 KB
- Phyto tinybluegreen.jpg 599 × 394; 58 KB
- Phytoplankton - the foundation of the oceanic food chain 560x396.jpg 560 × 396; 101 KB
- Phytoplankton - the foundation of the oceanic food chain m.jpg 720 × 508; 170 KB
- Phytoplankton - the foundation of the oceanic food chain.jpg 3,972 × 2,676; 5.44 MB
- Phytoplankton decline NASA study Sept2015.png 1,032 × 784; 522 KB
- Phytoplankton kamchatka NASA.jpg 720 × 360; 49 KB
- Phytoplankton-Phytopedia 2016.png 799 × 695; 732 KB
- Phytoplankton.jpg 600 × 600; 97 KB
- Planet home page-2022.png 800 × 400; 392 KB
- Plankton - phytoplankton m.jpg 773 × 558; 364 KB
- Plankton Phytoplankton--'Climate Dance'.jpg 773 × 644; 161 KB
- Plankton story - New Yorker - Oct 2021.jpg 619 × 737; 125 KB
- Plankton swirl Jan 2015.jpg 720 × 480; 161 KB
- Plankton.jpg 400 × 259; 34 KB
- Planktonbluegreen tinyones.jpg 640 × 320; 99 KB
- Planting Corals Now.jpg 800 × 365; 72 KB
- Prochlorococcus blue-green.png 501 × 273; 86 KB
- Prochlorococcus blue-green.tiny ones.png 505 × 277; 130 KB
- Prochlorococcus featured at GreenPolicy360.png 497 × 642; 42 KB
- Racing Extinction websiteplankton 2.jpg 170 × 170; 10 KB
- Racing Extinction websiteplankton.jpg 664 × 360; 141 KB
- Rain Garden Design courtesy of www.PermaDesign.com Nate Downey.png 800 × 614; 601 KB
- Recent Satellite Imagery of Earth - via Azavea.png 600 × 747; 488 KB
- Rosalind Franklin.jpg 521 × 626; 40 KB
- Seagrass florida keys-noaa.jpg 700 × 267; 65 KB
- Shifting Baseline Syndrome - threats to ecosystems biodiversity.png 431 × 534; 322 KB
- Shifting Baselines 2.jpg 600 × 600; 140 KB
- SOBEK - OARS adventuring.png 800 × 534; 969 KB
- Tara Expedition.png 700 × 437; 697 KB
- The World Is Blue.jpg 340 × 499; 40 KB
- Thriving on Our Changing Planet.png 495 × 369; 244 KB
- Tiny Plankton - via The Guardian.jpg 591 × 181; 59 KB
- Toby Hemenway-RIP Dec2016.png 503 × 327; 32 KB
- US River basins - watersheds.jpg 800 × 477; 131 KB
- Worldwide view of oceans phytoplankton earth observatory nasa.gif 540 × 270; 0 bytes
- Worldwide view of plankton www.phys.org.jpg 378 × 200; 138 KB