Category:Clean Water: Difference between revisions
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Siterunner (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
'''''Common Pollutants''''' | '''''Common Pollutants''''' | ||
: • Nutrients: Nitrogen & phosphorous (fertilizers, animal wastes, septic discharge) | |||
: • Man-Made Chemicals: Pesticides & herbicides | |||
: • Pathogens: Bacteria & Viruses from pet waste and failing septic systems | |||
: • Metals: Copper, Lead, Mercury, Chromium in car brake linings and tires | |||
: • Hydrocarbons: Gasoline and Oil leaks from faulty tanks and improper disposal | |||
: • Sediments: Dirt from road runoff and construction sites | |||
: • Organic Materials: Oxygen depleting Leaves, Grass Clippings, Plant Materials | |||
: • Trash and Debris: Litter is aesthetically unappealing and a hazard to wildlife | |||
[[Category:Water]] | [[Category:Water]] | ||
Revision as of 17:05, 3 February 2017
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clean_Water_Act
https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-clean-water-act
Clean Water Act
Congress first passed the Federal Water Pollution Control Act in 1972. Amending the law five years later in what became known as the “Clean Water Act” Congress regulated by permit all end-of-pipe or "Point Source" discharges to navigable waters of the United States. In 1987, it extended the Clean Water Act to cover indirect or “Non-Point Source” pollution, most prevalent in stormwater runoff.
Stormwater Runoff
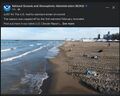
Stormwater runoff is water from rain or melting snow that flows from roofs, paved roads and parking lots, bare soil, and sloped lawns that cannot be absorbed in the ground. As it flows, the runoff collects pollutants like fertilizers, pesticides, oil and grease, animal wastes and sediments and carries them directly to coastal waters or to storm drains, which, in the case of coastal communities, often discharge to harbor waters. These pollutants restrict recreational use and degrade the marine habitat resulting in bathing beach closures and shellfish harvesting restrictions.
Common Pollutants
- • Nutrients: Nitrogen & phosphorous (fertilizers, animal wastes, septic discharge)
- • Man-Made Chemicals: Pesticides & herbicides
- • Pathogens: Bacteria & Viruses from pet waste and failing septic systems
- • Metals: Copper, Lead, Mercury, Chromium in car brake linings and tires
- • Hydrocarbons: Gasoline and Oil leaks from faulty tanks and improper disposal
- • Sediments: Dirt from road runoff and construction sites
- • Organic Materials: Oxygen depleting Leaves, Grass Clippings, Plant Materials
- • Trash and Debris: Litter is aesthetically unappealing and a hazard to wildlife
Subcategories
This category has the following 13 subcategories, out of 13 total.
Pages in category "Clean Water"
The following 52 pages are in this category, out of 52 total.
C
E
G
- Generation Green
- George E. Brown Jr
- Going Green: Texas v. Pennsylvania
- Google Earth Timelapse
- Green Bank in Maryland - and More
- Green Best Practices
- Green New Deal
- Green Party
- Green Stories of the Day
- Green Stories of the Day - GreenPolicy360 Archive
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2013
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2014
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2015
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2016
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2017
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2018
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2019
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2020
- GreenPolicy360 Archive Highlights 2023
Media in category "Clean Water"
The following 200 files are in this category, out of 236 total.
(previous page) (next page)- 1977 from the Office of Science and Technology Policy.jpg 661 × 711; 177 KB
- 3M lawsuit re forever chemicals - June 2023.png 603 × 600; 357 KB
- A Planet Citizen View.png 799 × 1,241; 1.64 MB
- A scorching year, what about the 360 warming data.jpg 600 × 706; 106 KB
- Acting to make a positive difference - in St Petersburg Florida.png 600 × 723; 645 KB
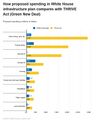
- American Jobs Act compared w THRIVE Act (Green New Deal).jpg 674 × 798; 90 KB
- Andrew Wheeler - EPA chief-coal industry lobbyist.jpg 640 × 352; 33 KB
- AOC March 26, 2019.jpg 597 × 433; 58 KB
- Aquifers global earth observations by grace20150616-16 m.jpg 800 × 450; 117 KB
- Arctic - Kolbert - 2023.png 553 × 476; 274 KB
- AskNatureAvatar s.png 200 × 200; 14 KB
- Astro POV - Mike Massimino - PlanetCitizen.png 800 × 466; 792 KB
- BantheBag California-OutinFront.png 519 × 715; 449 KB
- Battle for Democracy.jpg 640 × 123; 24 KB
- Be a planet citizen, make a choice, act to reduce climate change.jpg 1,024 × 595; 60 KB
- Bernie Sanders, Senate 2.PNG 800 × 517; 379 KB
- Bernie Sanders, Senate Aug 3.PNG 800 × 518; 388 KB
- Biden re Earth Day 2023.png 640 × 400; 155 KB
- Biden-Harris, CNN News Online - Nov 8, 2020.jpg 800 × 484; 114 KB
- Big Wobble 2020.jpg 507 × 342; 79 KB
- Biggest climate related legislation in history - 1.png 800 × 188; 68 KB
- Bill Nye The Planet's on Fire.jpg 800 × 675; 106 KB
- Bloomberg Environment-water rules to change.png 800 × 429; 329 KB
- Blue Marble photo taken by the crew of Apollo 17 (1972).jpg 642 × 605; 129 KB
- Blueoceanwaves.png 983 × 579; 857 KB
- California at the forefront of US environmental policies.png 600 × 450; 50 KB
- Canary - 1.jpg 448 × 901; 144 KB
- Canary - 2.png 446 × 531; 264 KB
- Carbon Footprint - BP-McKibben-Solnit-Aug2021.jpg 516 × 264; 66 KB
- Cardinal directions m.png 250 × 250; 20 KB
- Carl Sagan at the Emerging Issues Forum - 1990.png 360 × 460; 192 KB
- Carl Sagan at the Emerging Issues Forum.png 747 × 600; 600 KB
- Carl Sagan, the atmosphere unifies and connects all of our world.png 360 × 390; 229 KB
- Caroline Lucas-Green New Deal.jpg 584 × 391; 71 KB
- Challenge of Acting for the Commons.png 700 × 548; 175 KB
- ChatGPT talks of fighting climate denialism.png 707 × 747; 239 KB
- Citizens Climate Lobby - Save Our Future Act 2021.jpg 518 × 262; 77 KB
- Clean water E4C.jpg 616 × 302; 44 KB
- Climate Change COP27 - Nov 11 2022 US Representatives.jpg 712 × 444; 54 KB
- Climate Change COP27 - Nov 11 Kathy Castor.jpg 712 × 710; 77 KB
- Climate Emergency Institute - Oct 2022.png 610 × 600; 274 KB
- Climate News - Oct 28 2022.jpg 626 × 600; 88 KB
- Climate News Dec 4 2023 in Dubai.png 800 × 1,037; 649 KB
- Climate Plans Enforcement - Resources - GreenPolicy.png 768 × 897; 686 KB
- Climate poll - Florida.png 640 × 267; 36 KB
- Commons-concepts permanent culture now s.png 448 × 211; 75 KB
- Commons-concepts permanent culture now.png 830 × 391; 39 KB
- Congressman george.e.brown.gif 235 × 305; 41 KB
- COP27 'opening speech'.png 640 × 460; 160 KB
- COP28 News - Dec 13 2023.png 800 × 898; 410 KB
- Cousteau - clean air and water.png 649 × 300; 254 KB
- Cradle of Civilization - and climate change.jpg 640 × 360; 70 KB
- Dan Ellsberg - 2017.png 503 × 548; 101 KB
- David-brower-environmental-movement-cover.jpg 530 × 800; 89 KB
- Disaster scenarios raise the stakes for Colorado River - 1.png 640 × 213; 56 KB
- Disaster scenarios raise the stakes for Colorado River - 2.png 640 × 154; 14 KB
- DJT - US message to world.jpg 800 × 266; 45 KB
- Dr Volts talks of lawns and their problems.jpg 492 × 376; 49 KB
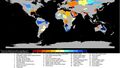
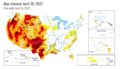
- Drought Monitor Map - April 2022.png 800 × 459; 238 KB
- Earth Day - DSCOVR-EPIC 2019.jpg 800 × 772; 150 KB
- Earth Day 2022 - Act up.png 457 × 370; 155 KB
- Earth Day Flag.png 400 × 267; 69 KB
- Earth Day memories.png 800 × 210; 381 KB
- Earth-Day-flag.jpg 600 × 480; 31 KB
- Earths rotation as we roll thru space.jpg 800 × 529; 69 KB
- EarthScience Missions via the EOS - 2022.png 800 × 219; 139 KB
- Env policy laws US 'the beginning' of env era.jpg 370 × 345; 65 KB
- Env protection on the way out Jan2018 summary.png 418 × 789; 57 KB
- Env protection on the way out Jan2018.png 582 × 522; 48 KB
- Envir earth day 1970.jpg 197 × 295; 13 KB
- Environmental Justice and Environmental Law.jpg 274 × 668; 108 KB
- Environmental Protection Agency logo.png 380 × 414; 39 KB
- Environmental Studies-Documerica.png 688 × 963; 522 KB
- EPA .jpg 640 × 360; 15 KB
- EPA and the Green Bank - Feb 2023.png 476 × 542; 244 KB
- EPA History Xin Liu-2010.pdf ; 2.88 MB
- ESG Fight - Feb 2023.png 396 × 194; 88 KB
- Estuary in Clearwater on Tampa Bay.jpg 3,584 × 2,016; 1.5 MB
- European Greens - Baerbock - Candidate for German Chancellorship.jpg 513 × 185; 37 KB
- European Greens EGPCongress Dec 2022.png 800 × 745; 640 KB
- EWG Tap Water Database.png 640 × 432; 59 KB
- Fact Checking organizations at work.jpg 800 × 390; 44 KB
- Facts Count-WaPo Reports-19127 false-misleading claims in 1226 days.jpg 601 × 489; 100 KB
- Florida at crossroads-Turning the Toxic Tide.png 800 × 666; 984 KB
- Florida via NASA 2022.png 800 × 1,020; 1.12 MB
- Florida Wildlife Corridor - 2022 illustration.png 800 × 628; 473 KB
- Florida Wildlife Corridor FLWC Water Benefits December 2022.png 768 × 886; 109 KB
- Fox on Earth Day 2023.jpg 640 × 275; 58 KB
- G Earth Outreach.jpg 800 × 412; 44 KB
- G7 Climate News.png 640 × 205; 125 KB
- G7 DJTclimatetweet.png 640 × 300; 45 KB
- G7 Split-2017.png 800 × 182; 177 KB
- G7-Climate-2017.png 800 × 136; 66 KB
- G7-Climate-News.png 640 × 317; 176 KB
- Gavin in Glasgow - Nov 10 2021.png 728 × 600; 378 KB
- Gavin Schmidt - NASA - January 2022.png 451 × 436; 150 KB
- George Brown 1969-Reflections on US Role in the World.png 700 × 372; 99 KB
- George Brown, Sci Com't.jpg 200 × 200; 7 KB
- German foreign minister travels to India.png 640 × 178; 115 KB
- Ginsburg leaves a chasm on the Supreme Court.jpg 800 × 624; 92 KB
- Global Climate Action Summit.png 640 × 400; 470 KB
- Global climate conferences and GHG increases.jpg 793 × 801; 56 KB
- Global Green New Deal.jpg 427 × 640; 32 KB
- Global Stocktake, the first GST.jpg 800 × 905; 513 KB
- Google Earth Engine.png 448 × 165; 45 KB
- Green Collar Economy.jpg 100 × 160; 6 KB
- Green Networking @GreenPolicy360.net.png 788 × 604; 764 KB
- Green New Deal - Bloomberg Jan 29,2019.png 640 × 757; 589 KB
- Green New Deal - Resolution.pdf ; 55 KB
- Green New Deal - Strategic Demands - Oct 1, 2021.png 602 × 658; 245 KB
- Green-New-Deal-December-2018-1.png 800 × 634; 207 KB
- Greeneuropeanjournal.eu.jpg 485 × 237; 30 KB
- Groundwaterstudy 1.png 800 × 384; 237 KB
- Harvest the Rain cover .png 582 × 800; 1.06 MB
- Harvest the Rain reviews.png 800 × 879; 306 KB
- Historic climate-clean energy vote in US Congress August 12 2022.jpeg 800 × 775; 384 KB
- Huge heat anomaly in 2023 - by Gavin Schmidt.png 735 × 857; 172 KB
- Human history, as an 800 page book.jpg 799 × 1,112; 148 KB
- IEA - Support for Fossil Fuels - re 2021.jpg 559 × 800; 143 KB
- In Love with Earth.jpg 328 × 499; 15 KB
- In nature, nothing exists alone.jpg 500 × 357; 26 KB
- Joan and Christiana - April 2022.png 486 × 460; 282 KB
- Joe Biden is projected winner Nov7-2020.jpg 343 × 120; 26 KB
- Kathy-castor-tampa-bay-florida.jpg 750 × 600; 41 KB
- LA Times - July 2023 on the world's response to the climate crisis-1a.png 800 × 1,011; 657 KB
- LA Times on the world's response to the climate crisis-2.png 800 × 651; 297 KB
- LA Times on the world's response to the climate crisis-3.png 800 × 806; 302 KB
- LA Times on the world's response to the climate crisis-4.png 800 × 896; 321 KB
- Landsat Image Gallery.jpg 800 × 766; 187 KB
- Le Grand Bleu.png 738 × 1,107; 1.52 MB
- Lifestraw.png 703 × 344; 605 KB
- Limits to Growth screenshot-30yr-40yr updates.png 448 × 329; 108 KB
- Living Earth.png 441 × 183; 106 KB
- Los-angeles-smog-1970s.jpg 800 × 438; 19 KB
- Manchin again - July 15 2022.png 600 × 654; 523 KB
- Mapping changes in global temperature 1850-2022.png 656 × 680; 180 KB
- March for Science-1.png 800 × 291; 596 KB
- Memories of Big Science advocates in the US Congress.jpg 583 × 279; 87 KB
- Methane cuts pledge - COP27.png 399 × 336; 164 KB
- Methane Reduction proposal passes in EU Parliament - May 2023.png 620 × 600; 552 KB
- Michael Mann, planet citizen.png 604 × 835; 273 KB
- Monitoring Greenhouse Gases from Satellite Missions 2021-2030.png 801 × 386; 143 KB
- Montana climate trial News - 2023-08-14.png 789 × 768; 389 KB
- Multispectral Scanning Systen - MSS.jpg 688 × 587; 103 KB
- NASA and micro nano sats.png 443 × 431; 43 KB
- NASA has a new mission... against Methane.png 800 × 576; 681 KB
- NASA test mission to protect earth from asteroid - Nov 2021.png 508 × 800; 424 KB
- Navigate with Knowledge - StratDem - GreenPolicy360.jpg 800 × 534; 62 KB
- Nelson, the oil spill and the student anti-war movement.png 600 × 457; 529 KB
- New Economics Foundation logo.png 476 × 123; 9 KB
- NOAA - NCEI report on US temps 2023-2024.jpg 600 × 561; 109 KB
- NOAA report on heat records broken in US - 2023.jpg 600 × 480; 229 KB
- OaklandWastewater plant.jpg 800 × 399; 125 KB
- Our Fragile Moment.jpg 612 × 480; 80 KB
- Our Fragile Moment.png 301 × 448; 360 KB
- PFAS - 1.png 640 × 335; 177 KB
- PFAS - 2.png 800 × 858; 744 KB
- Piece of a Protoplanet.jpg 632 × 600; 69 KB
- Planet Dove satellite image over Dubai.png 800 × 791; 1.58 MB
- PlanetCitizen - Your Moment on Earth.jpg 650 × 625; 80 KB
- Poverty 2019.jpg 800 × 673; 91 KB
- Protect Democracy.png 775 × 600; 727 KB
- RBG as mom.jpg 320 × 320; 11 KB
- RBG as student.jpg 480 × 600; 27 KB
- RBG at Harvard Law School.jpg 640 × 942; 42 KB
- Rebuild the Dream.jpg 100 × 160; 6 KB
- Record tumble - climate change.png 727 × 333; 27 KB
- Republican Party 2024 Climate Strategy.png 589 × 344; 44 KB
- Robert W Kates.jpg 400 × 231; 43 KB
- Scott Pruitt - running for James Inhofe Senate seat - Apr 2022.png 585 × 480; 281 KB
- Scott pruitt epa.jpg 640 × 427; 41 KB
- SCOTUS decision on water protection.png 535 × 424; 299 KB
- Shell lawsuit Feb 2023.png 768 × 534; 229 KB
- Shrinking earth.jpg 762 × 600; 167 KB
- Shrinking the Earth, The Rise and Decline of Natural Abundance.jpg 180 × 274; 10 KB
- Small Is Beautiful 1973.jpg 257 × 388; 17 KB
- Speed and Scale Action Plan.png 550 × 867; 132 KB
- Speed and Scale Poster.png 490 × 772; 101 KB
- Steven J Schmidt, May 2023.png 363 × 484; 383 KB
- Story telling and science education.png 515 × 480; 171 KB
- Surprise climate deal.png 589 × 735; 83 KB